https://sites.google.com/site/physiolablist/
The Objectives for this lab are:
- To list at least three functions of the skeletal system.
- To identify the four main kinds of bones.
- To identify surface bone markings and their function.
- To identify the major anatomical areas on a longitudinally cut long bone (or diagram of one).
- To identify the major regions and structures of an osteon in a histological specimen of compact bone (or diagram or model of one).
- To explain the role of the inorganic slats and organic matrix in providing flexibility and hardness to bone.
Hypotheses & Procedures
Part 1: Bone Markings & Classification.
If students examine a variety of disarticulated bones then they will be able to classify them into one of the four anatomical groups: long, short, flat, or irregular and point out examples of bone markings.
Part 2: Gross Anatomy of the Typical Long Bone.
If students examine a fresh cut bone as well as a cleaned dry bone that has been cut along its longitudinal axis, then they will be able to identify the major anatomical structures of a bone as an organ.
Part 3 Microscopic Structure of Compact Bone.
If students observe a prepared slide of ground bone as well as a model of microscopic compact bone, then they will be able to identify the major regions and structures of an osteon.
Part 4: Chemical Composition of Bone:
If students observe a sample of bone that has been baked then they will be able to identify the role of the organic compounds in bone because baking removes the collagen fibers of the matrix.
If students observe a sample of bone that has been soaked in acid then they will be able to identify the role of the inorganic compounds in bone because acids dissolve the calcium salts.
Materials (on lab sheet)
Experiment/Data and lab questions
Part 1: Bone Markings & Classification.
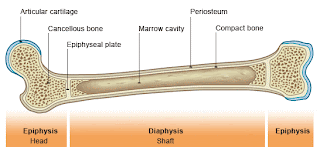
Part 2: Gross Anatomy of the Typical Long Bone.
The pointer is showing the hyaline cartalige that helps the joints move with out friction.
Part 3 Microscopic Structure of Compact Bone.
Copy/paste this image into a draw program (like MS Paint). Label the parts of the osteon that you can identify. Save the image and use it to replace the unlabeled one into your blog, .
I CANNOT FIND A PAINT PROGRAM ON MY COMPUTER
I CANNOT FIND A PAINT PROGRAM ON MY COMPUTER
Part 4: Chemical Composition of Bone:
Do treated bones retain the structure of untreated specimens?
Describe what happened to the matrix when the bone was baked. How does this bone feel?
When the bone was baked, the collagen was removed from the bone and it became harder rougher than a normal bone.
Describe what happened to the matrix when the bone was soaked in acid. How does this bone feel?
When the bone was soaked in acid, the calcium from the bone was taken from the bone and mixed with the acid making a milky white cloud mixture. The bone feels softer than a bone should.
Optional: Include a video of your lab team demonstrating the effects of baking and acid on the matrix of bone.
Describe what happened to the matrix when the bone was soaked in acid. How does this bone feel?
When the bone was soaked in acid, the calcium from the bone was taken from the bone and mixed with the acid making a milky white cloud mixture. The bone feels softer than a bone should.
Optional: Include a video of your lab team demonstrating the effects of baking and acid on the matrix of bone.
Conclusion:
- List at least three functions of the skeletal system. it provides the shape and form for our bodies in addition to supporting, protecting, allowing bodily movement, producing blood for the body, and storing minerals.
- Identify the four main kinds of bones. Long, short, irregular, and flat.
- Which surface bone markings and their function can you identify and describe?Condyle which is also the head of the bone, and the foramen which is where blood vessels, ligaments, or nerves go through.
- Which major anatomical areas on a longitudinally cut long bone (or diagram of one) can you identify?On a long bone, The ends are called the epiphysis and the long shaft part is called the diaphysis. There is spongy bone which is usually around the epiphysis parts. There is an epiphylial line that shows how much taller you will grow and if you are done growing or not.
- Which major regions and structures of an osteon in a histological specimen of compact bone (or diagram or model of one) can you identify? There are the rings of lamellae, the lacuna where osteocytes are found, and the central canal which carries blood vessels and nerves.
- Explain the role of the inorganic slats and organic matrix in providing flexibility and hardness to bone. The inorganic salts provide hardness to the bone and the organic matrix provides flexibility to the bone particularly the collagen fibers.